by TeachThought Employees
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Verbs (with AI-Conscious Classroom Examples)
Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Verbs adapt Bloom’s cognitive framework for digital studying. Every stage—from remembering to creating—pairs with purposeful expertise actions (together with AI) so the main target stays on considering moderately than instruments.
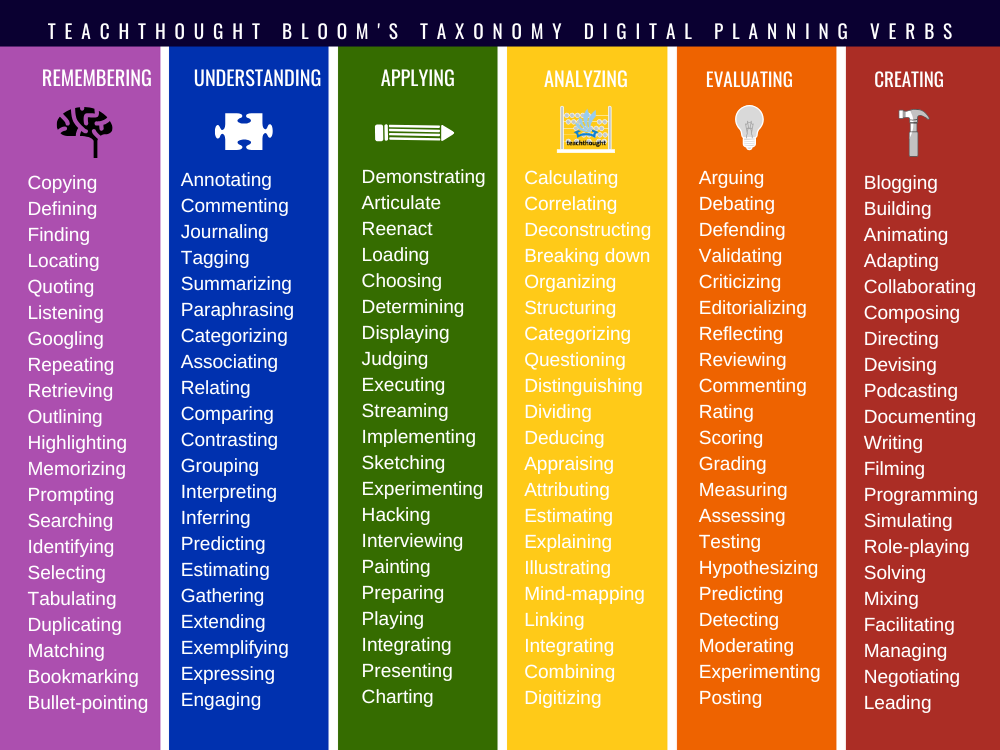
Remembering
Recall, retrieve, or acknowledge info and definitions.
- Recall: Listing key phrases for a unit glossary.
- Find: Discover a primary-source quote supporting a declare.
- Bookmark: Save credible sources to a shared assortment.
- Tag: Apply correct key phrases to arrange assets.
- Retrieve: Use spaced-repetition/flashcards to overview formulation.
- Immediate (recall): Ask an AI to restate definitions from class notes, then confirm with sources.
Understanding
Clarify, summarize, interpret, and evaluate concepts.
- Summarize: Write a concise summary of a podcast episode.
- Paraphrase: Reword a dense paragraph to make clear which means.
- Annotate: Add notes that designate theme and proof in a shared doc.
- Evaluate: Construct a side-by-side chart of two insurance policies.
- Clarify: File a brief screencast explaining a course of.
- Immediate (clarify): Ask an AI to elucidate an idea at two grade ranges; cite-check claims.
Making use of
Use data to carry out duties, resolve issues, or produce artifacts.
- Reveal: File a labored instance fixing a quadratic.
- Execute: Run a simulation and report outcomes.
- Prototype: Construct a low-fidelity mannequin in Slides or Canva.
- Code: Write a brief script to remodel or validate knowledge.
- Apply rubric: Rating a pattern product utilizing standards.
- Refine immediate: Iteratively modify an AI immediate to satisfy constraints (viewers, size, citations).
Analyzing
Break ideas aside, establish patterns and relationships, look at construction.
- Analyze: Evaluate two editorials for bias utilizing an proof guidelines.
- Arrange: Create a timeline that separates causes and results.
- Classify: Type claims, proof, and reasoning into classes.
- Visualize: Construct charts that reveal tendencies in a dataset.
- Hint sources: Confirm quotes and attributions again to originals.
- Evaluate fashions: Consider two AI outputs on accuracy and transparency.
Evaluating
Choose high quality, justify choices, and defend positions utilizing standards.
- Critique: Present evidence-based suggestions on a peer draft.
- Validate: Reality-check statistics and cite authoritative sources.
- Average: Facilitate a category dialogue for relevance and respect.
- A/B consider: Take a look at two options and justify the stronger alternative.
- Purple-team: Stress-test an AI-generated plan for dangers and inaccuracies.
- Replicate: Write a course of observe justifying strategic selections with standards.
Creating
Synthesize concepts to provide authentic, purposeful work.
- Design: Plan a product with viewers, goal, and constraints.
- Compose: Produce a podcast/video explaining a real-world situation.
- Remix ethically: Remodel public-domain/CC media with attribution.
- Prototype (hi-fi): Construct a cultured artifact and user-test it.
- Chain (AI): Orchestrate multi-step AI duties (define → draft → cite-check → revision) with human oversight.
- Automate: Use easy scripts/AI brokers to streamline a workflow; doc limitations.
Continuously Requested Questions
How have been these verbs chosen?
They replicate frequent digital classroom actions mapped to Bloom’s ranges, up to date for credibility (platform-agnostic) and present follow (together with AI). Every verb features a transient instance so the cognitive intent is evident.
How ought to I assess these duties?
Pair every verb with standards that match the extent (e.g., evaluation requires proof patterns, not recall) and require college students to point out course of—planning notes, immediate logs, cite-checks, and revisions.
Bloom, B. S., Engelhart, M. D., Furst, E. J., Hill, W. H., & Krathwohl, D. R. (1956).
Taxonomy of Instructional Targets: The Classification of Instructional Objectives. Handbook I: Cognitive Area.
New York: David McKay Firm.
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (Eds.). (2001).
A Taxonomy for Studying, Instructing, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Instructional Targets.
New York: Longman.
Church buildings, A. (2009). Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy. (Variations emphasize aligning expertise duties to cognitive ranges moderately than particular instruments.)