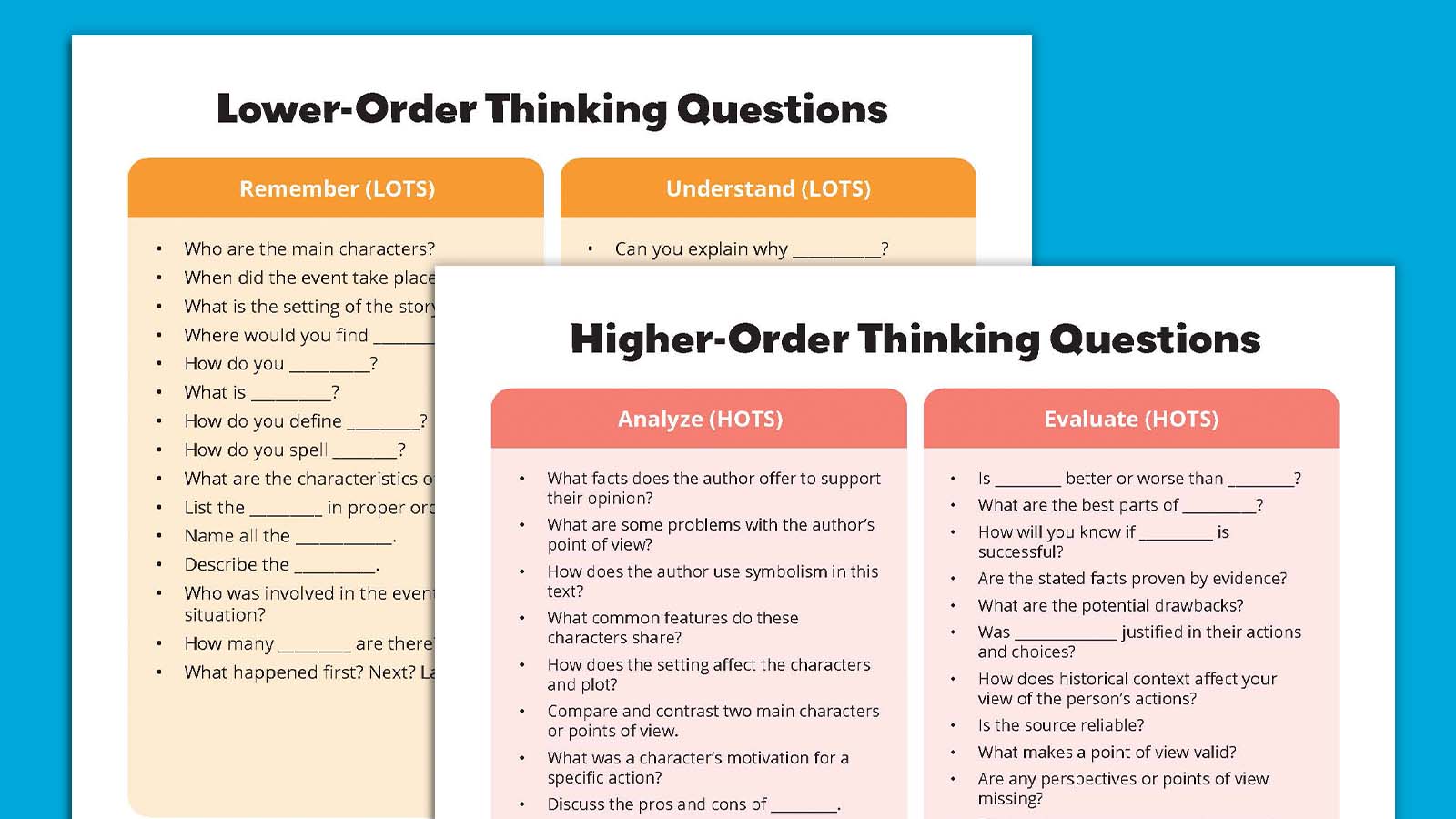
In a putting act of self-critique, one of many architects of the transformer know-how that powers ChatGPT, Claude, and just about each main AI system advised an viewers of business leaders this week that synthetic intelligence analysis has change into dangerously slim — and that he's shifting on from his personal creation.
Llion Jones, who co-authored the seminal 2017 paper "Consideration Is All You Want" and even coined the title "transformer," delivered an unusually candid evaluation on the TED AI convention in San Francisco on Tuesday: Regardless of unprecedented funding and expertise flooding into AI, the sector has calcified round a single architectural strategy, doubtlessly blinding researchers to the following main breakthrough.
"Although there's by no means been a lot curiosity and sources and cash and expertise, this has in some way triggered the narrowing of the analysis that we're doing," Jones advised the viewers. The wrongdoer, he argued, is the "immense quantity of stress" from traders demanding returns and researchers scrambling to face out in an overcrowded discipline.
The warning carries explicit weight given Jones's function in AI historical past. The transformer structure he helped develop at Google has change into the muse of the generative AI growth, enabling techniques that may write essays, generate photos, and have interaction in human-like dialog. His paper has been cited greater than 100,000 occasions, making it one of the crucial influential laptop science publications of the century.
Now, as CTO and co-founder of Tokyo-based Sakana AI, Jones is explicitly abandoning his personal creation. "I personally decided to start with of this 12 months that I'm going to drastically scale back the period of time that I spend on transformers," he mentioned. "I'm explicitly now exploring and on the lookout for the following huge factor."
Why extra AI funding has led to much less inventive analysis, in response to a transformer pioneer
Jones painted an image of an AI analysis neighborhood affected by what he known as a paradox: Extra sources have led to much less creativity. He described researchers continually checking whether or not they've been "scooped" by rivals engaged on equivalent concepts, and teachers selecting secure, publishable initiatives over dangerous, doubtlessly transformative ones.
"For those who're doing normal AI analysis proper now, you type of should assume that there's possibly three or 4 different teams doing one thing very comparable, or possibly precisely the identical," Jones mentioned, describing an atmosphere the place "sadly, this stress damages the science, as a result of persons are speeding their papers, and it's decreasing the quantity of creativity."
He drew an analogy from AI itself — the "exploration versus exploitation" trade-off that governs how algorithms seek for options. When a system exploits an excessive amount of and explores too little, it finds mediocre native options whereas lacking superior options. "We’re nearly definitely in that scenario proper now within the AI business," Jones argued.
The implications are sobering. Jones recalled the interval simply earlier than transformers emerged, when researchers had been endlessly tweaking recurrent neural networks — the earlier dominant structure — for incremental beneficial properties. As soon as transformers arrived, all that work all of a sudden appeared irrelevant. "How a lot time do you assume these researchers would have spent attempting to enhance the recurrent neural community in the event that they knew one thing like transformers was across the nook?" he requested.
He worries the sector is repeating that sample. "I'm apprehensive that we're in that scenario proper now the place we're simply concentrating on one structure and simply permuting it and attempting various things, the place there could be a breakthrough simply across the nook."
How the 'Consideration is all you want' paper was born from freedom, not stress
To underscore his level, Jones described the circumstances that allowed transformers to emerge within the first place — a stark distinction to right this moment's atmosphere. The venture, he mentioned, was "very natural, backside up," born from "speaking over lunch or scrawling randomly on the whiteboard within the workplace."
Critically, "we didn't even have a good suggestion, we had the liberty to truly spend time and go and work on it, and much more importantly, we didn't have any stress that was coming down from administration," Jones recounted. "No stress to work on any explicit venture, publish numerous papers to push a sure metric up."
That freedom, Jones urged, is essentially absent right this moment. Even researchers recruited for astronomical salaries — "actually one million {dollars} a 12 months, in some instances" — might not really feel empowered to take dangers. "Do you assume that after they begin their new place they really feel empowered to strive their wild concepts and extra speculative concepts, or do they really feel immense stress to show their price and as soon as once more, go for the low hanging fruit?" he requested.
Why one AI lab is betting that analysis freedom beats million-dollar salaries
Jones's proposed answer is intentionally provocative: Flip up the "discover dial" and brazenly share findings, even at aggressive price. He acknowledged the irony of his place. "It could sound just a little controversial to listen to one of many Transformers authors stand on stage and inform you that he's completely sick of them, nevertheless it's type of honest sufficient, proper? I've been engaged on them longer than anybody, with the doable exception of seven individuals."
At Sakana AI, Jones mentioned he's trying to recreate that pre-transformer atmosphere, with nature-inspired analysis and minimal stress to chase publications or compete straight with rivals. He supplied researchers a mantra from engineer Brian Cheung: "You need to solely do the analysis that wouldn't occur when you weren't doing it."
One instance is Sakana's "steady thought machine," which contains brain-like synchronization into neural networks. An worker who pitched the concept advised Jones he would have confronted skepticism and stress to not waste time at earlier employers or educational positions. At Sakana, Jones gave him every week to discover. The venture grew to become profitable sufficient to be spotlighted at NeurIPS, a serious AI convention.
Jones even urged that freedom beats compensation in recruiting. "It's a very, actually great way of getting expertise," he mentioned of the exploratory atmosphere. "Give it some thought, gifted, clever individuals, bold individuals, will naturally hunt down this type of atmosphere."
The transformer's success could also be blocking AI's subsequent breakthrough
Maybe most provocatively, Jones urged transformers could also be victims of their very own success. "The truth that the present know-how is so highly effective and versatile… stopped us from on the lookout for higher," he mentioned. "It is smart that if the present know-how was worse, extra individuals can be on the lookout for higher."
He was cautious to make clear that he's not dismissing ongoing transformer analysis. "There's nonetheless loads of essential work to be executed on present know-how and bringing a variety of worth within the coming years," he mentioned. "I'm simply saying that given the quantity of expertise and sources that we’ve got presently, we will afford to do much more."
His final message was one in every of collaboration over competitors. "Genuinely, from my perspective, this isn’t a contest," Jones concluded. "All of us have the identical objective. All of us wish to see this know-how progress in order that we will all profit from it. So if we will all collectively flip up the discover dial after which brazenly share what we discover, we will get to our objective a lot sooner."
The excessive stakes of AI's exploration downside
The remarks arrive at a pivotal second for synthetic intelligence. The business grapples with mounting proof that merely constructing bigger transformer fashions could also be approaching diminishing returns. Main researchers have begun brazenly discussing whether or not the present paradigm has basic limitations, with some suggesting that architectural improvements — not simply scale — might be wanted for continued progress towards extra succesful AI techniques.
Jones's warning means that discovering these improvements might require dismantling the very incentive constructions which have pushed AI's latest growth. With tens of billions of {dollars} flowing into AI growth yearly and fierce competitors amongst labs driving secrecy and speedy publication cycles, the exploratory analysis atmosphere he described appears more and more distant.
But his insider perspective carries uncommon weight. As somebody who helped create the know-how now dominating the sector, Jones understands each what it takes to attain breakthrough innovation and what the business dangers by abandoning that strategy. His resolution to stroll away from transformers — the structure that made his popularity — provides credibility to a message which may in any other case sound like contrarian positioning.
Whether or not AI's energy gamers will heed the decision stays unsure. However Jones supplied a pointed reminder of what's at stake: The following transformer-scale breakthrough could possibly be simply across the nook, pursued by researchers with the liberty to discover. Or it could possibly be languishing unexplored whereas 1000’s of researchers race to publish incremental enhancements on structure that, in Jones's phrases, one in every of its creators is "completely sick of."
In any case, he's been engaged on transformers longer than nearly anybody. He would know when it's time to maneuver on.